Bite registration material
Bite registration material
Bite registration is an extremely important step in the fabrication of diagnostic models, restorations, bite-raising appliances, orthodontic appliances etc. It is used for precise, clear indexing of the three-dimensional alignment of maxilla and mandible in the required relationship.
 Bite registration material
Bite registration material
In addition to increasingly popular, yet technically still very costly primary digital (virtual) procedures, analogue registration methods are still mainly used today. Reversible thermoplastic (wax, resin, gutta percha), chemically-curing (ZnO, acrylics) and irreversible elastic (e.g. PVS = polyvinyl siloxane) bite registration materials are generally available for analogue registrations. These are applied either directly on natural or prosthetic opposing teeth or used for the fixation/indexing of custom-fabricated bite blocks, in full and partial denture prosthetics, for example in the form of an acrylic base (previously also shellac) with wax bite rims attached or as a connection between the upper and lower plates (acrylic, metal) in Gothic arch registration.
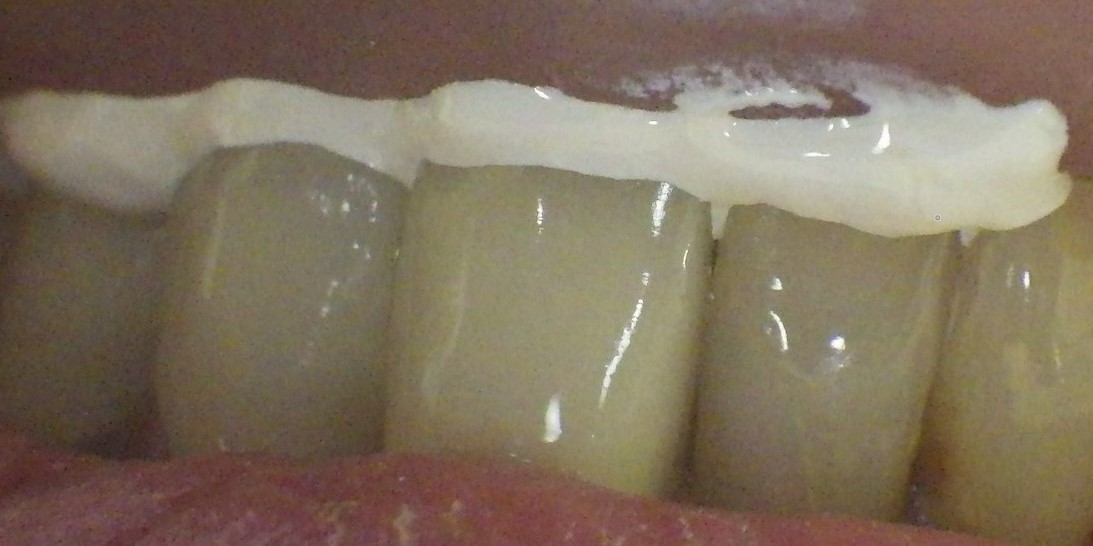 Zink oxide bite registration material
Zink oxide bite registration material
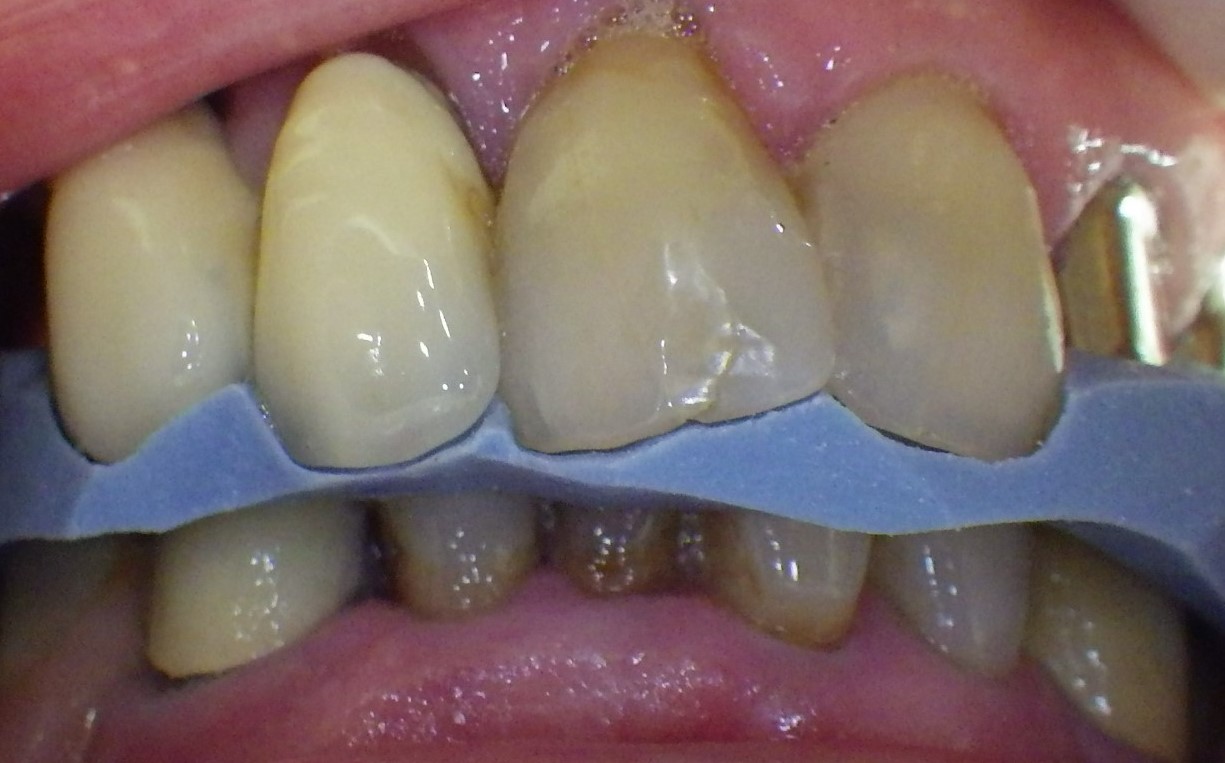 Silicone bite registration (check)
Silicone bite registration (check)
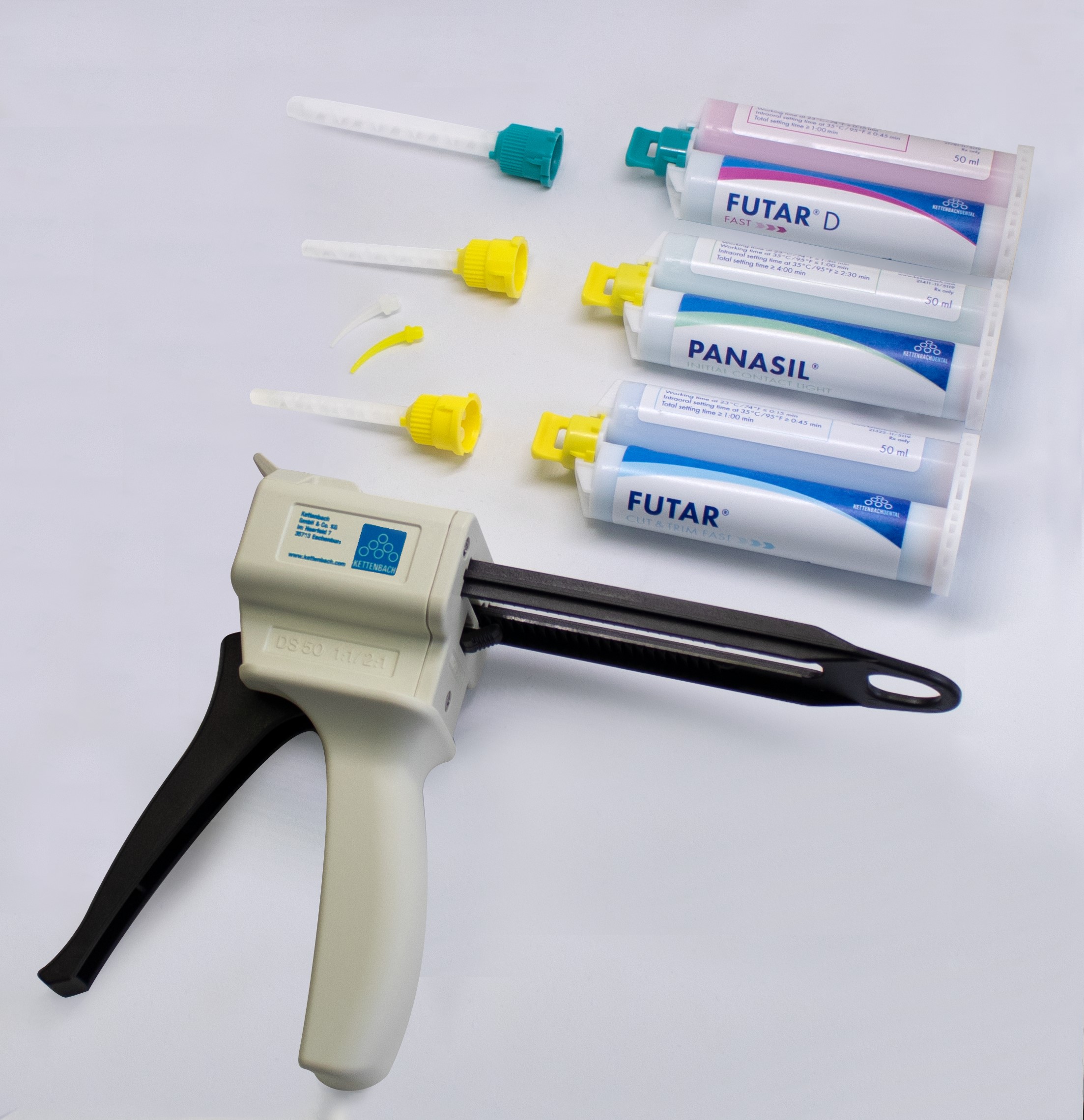
Addition-curing silicone bite registration materials (A-silicones), which are closely related to impression materials, offer the advantages of flowability (low bite resistance, avoids bite displacement) and positional stability (no uncontrolled flow) due to thixotropy, detailed representation (crisp details), dimensional stability (withdrawal from undercuts), thermal stability, good processability (grinding and/or trimming) and insensitivity to moisture or mechanical stress (compressive, tensile) after curing. Colour, transparency or opacity, setting time and final hardness (Shore A to Shore D), and scannability can be modified to a wide extent, depending on the area of application. They are used mainly as two-component bite registration materials (base + catalyst/activator) in standardised cartridges, which are mixed and applied using mixing guns and mixing tips.
Want to give it a try ...
... or need professional advice?
Get in touch with us or click Contact.
Word of the day
| English | German |
|---|---|
| platform-switching | Plattform-switching |
Focus text of the month
Composites also composite (from the Latin componere = to compose) are tooth-coloured filling materials with plastic properties used in dental treatment. In lay terms they are often referred to as plastic fillings, also erroneously sometimes confused with ceramic… Composites also composite (from the Latin componere = to compose) are tooth-coloured filling materials with plastic properties used in dental treatment. In lay terms they are often referred to as plastic fillings, also erroneously sometimes confused with ceramic fillings due to their tooth colour. After being placed in a cavity they cure chemically or by irradiating with light or a combination of the two (dual-curing). Nowadays, composites are also used as luting materials. The working time can be regulated with light-curing systems, which is a great advantage both when placing fillings and during adhesive luting of restorations. Dual-curing luting materials are paste/paste systems with chemical and photosensitive initiators, which enable adequate curing, even in areas in which light curing is not guaranteed or controllable. Composites were manufactured in 1962 by mixing dimethacrylate (epoxy resin and methacrylic acid) with silanized quartz powder (Bowen 1963). Due to their characteristics (aesthetics and advantages of the adhesive technique) composite restorations are now used instead of amalgam fillings.
The material consists of three constituents: the resin matrix (organic component), the fillers (inorganic component) and the composite phase. The resin matrix mainly consists of Bis-GMA (bisphenol-A-glycidyldimethacrylate). As Bis-GMA is highly viscous, it is mixed in a different composition with shorter-chain monomers such as, e.g. TEGDMA (triethylene glycol dimethacrylate). The lower the proportion of Bis-GMA and the higher the proportion of TEGDMA, the higher the polymerisation shrinkage (Gonçalves et al. 2008). The use of Bis-GMA with TEGDMA increases the tensile strength but reduces the flexural strength (Asmussen & Peutzfeldt 1998). Monomers can be released from the filling material. Longer light-curing results in a better conversion rate (linking of the individual monomers) and therefore to reduced monomer release (Sideriou & Achilias 2005) The fillers are made of quartz, ceramic and/ or silicon dioxide. An increase in the amount of filler materials results in decreases in polymerisation shrinkage, coefficient of linear expansion and water absorption. In contrast, with an increase in the filler proportion there is a general rise in the compressive and tensile strengths, modulus of elasticity and wear resistance (Kim et al. 2002). The filler content in a composite is also determined by the shape of the fillers.
Composite restorations Conclusion |

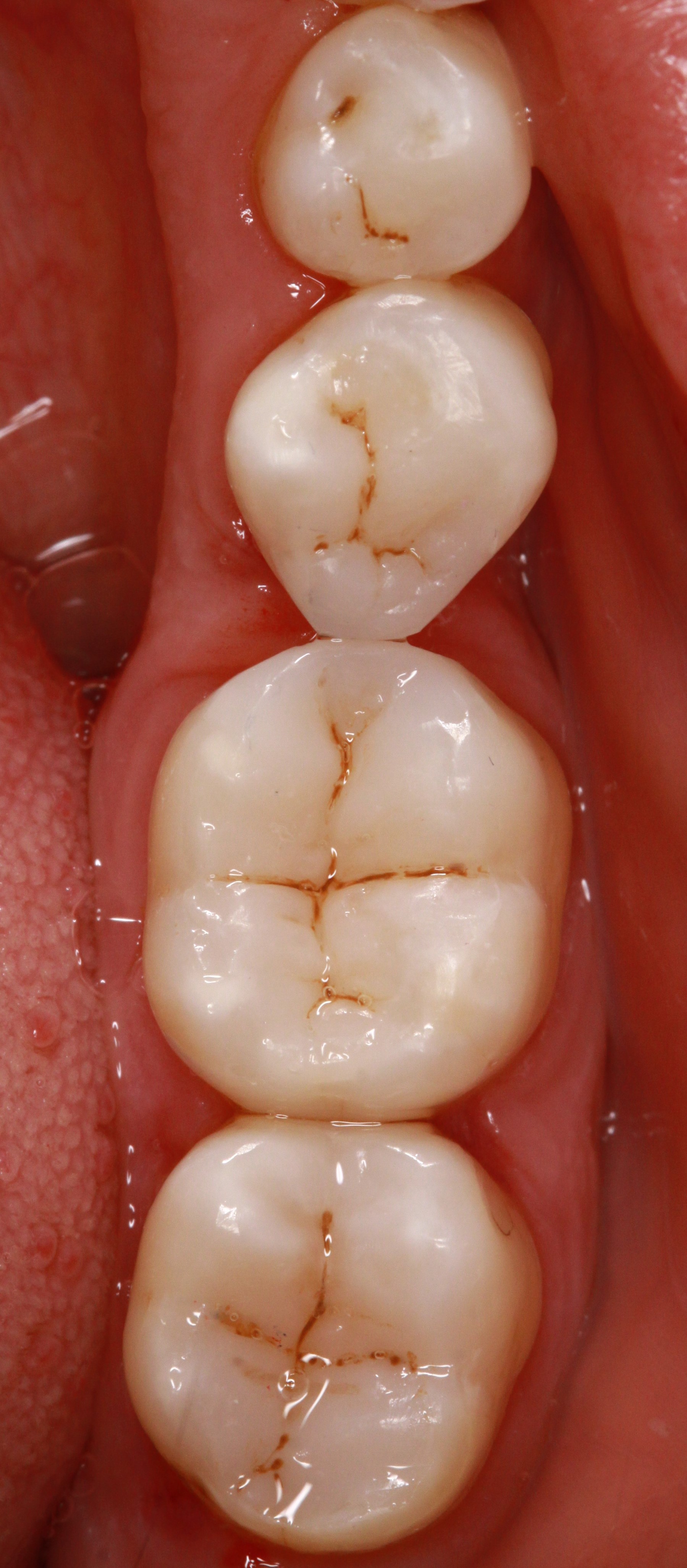
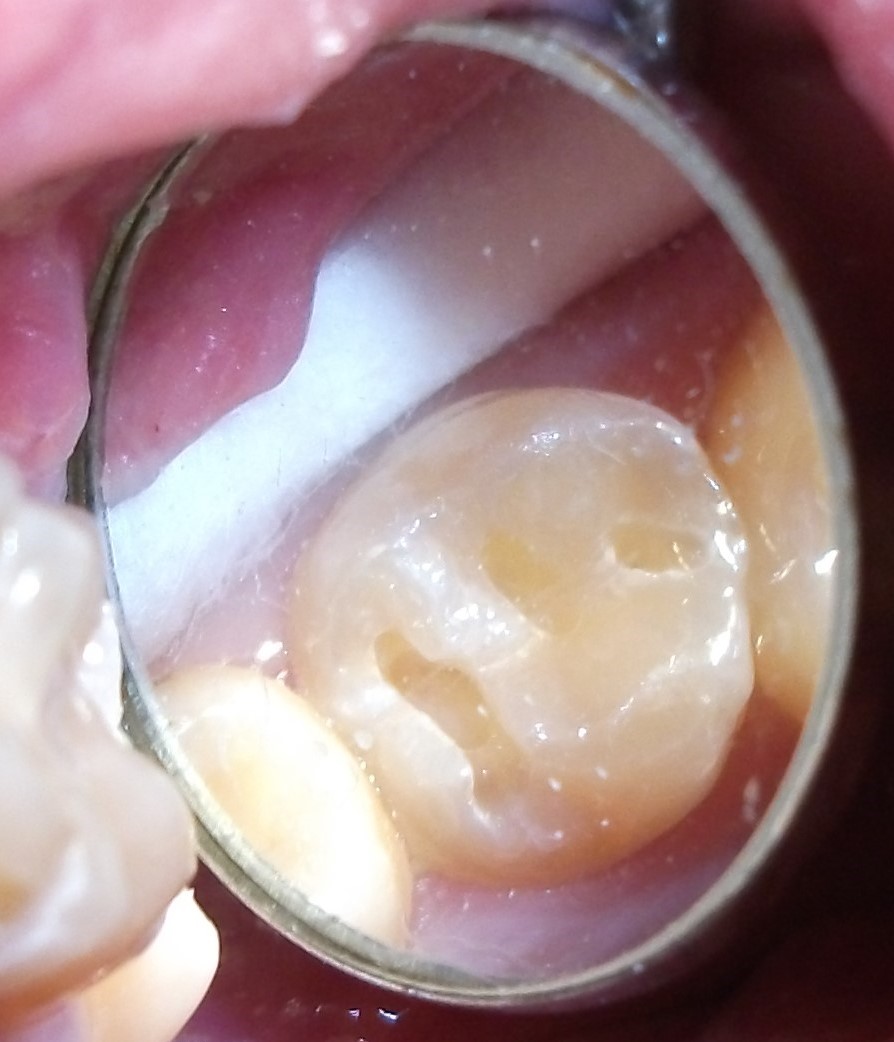 Minimally-invasive preparation and
Minimally-invasive preparation and 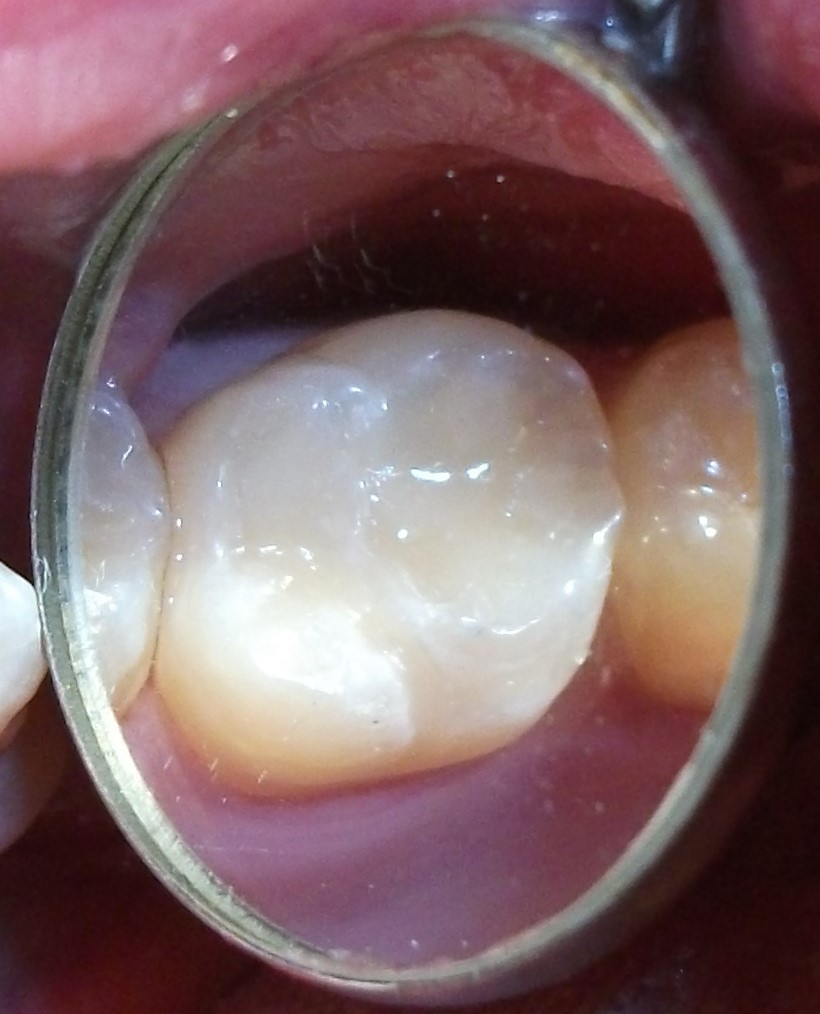 indiscernible composite restoration
indiscernible composite restoration